Table of Contents
Introduction to Bihar
In this article, I will discuss the geography of Bihar along with its administrative zones, climate, soils types river, etc. After reading this article on Bihar Geography, you will easily understand some of the basic information about Bihar, which is very important for the exam perspective like BPSC and BSSC.
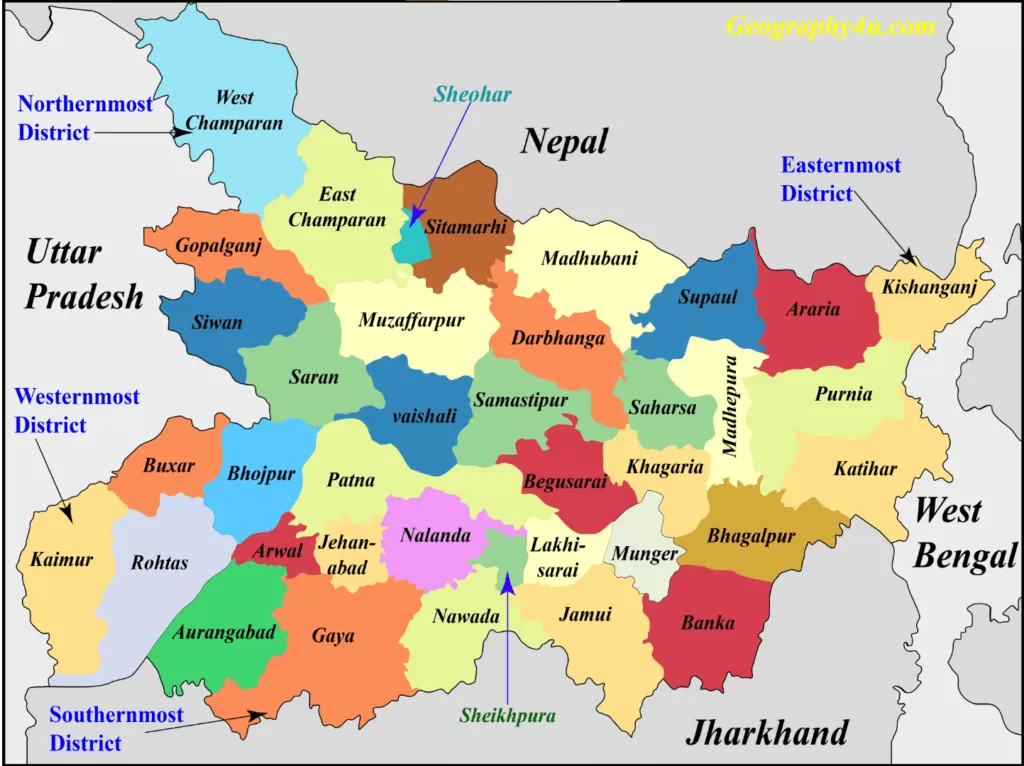
Geographically, Bihar is located in the eastern region of India. It is a land-locked state having boundaries with three Indian states namely Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand and West-Bengal. Bihar shares its border with Nepal in the north, Uttar Pradesh in the west, Jharkhand in the south and West Bengal in the south.
Average altitude- 52.73m above the mean sea level.
Bihar Location and Extent
| Sr. No. | Attributes | Facts |
| 1. | The latitudinal extent of Bihar | 24⁰ 20ꞌ 10″ N- 27⁰ 31ꞌ 15ꞌꞌ N. |
| 2. | The longitudinal extent of Bihar | 83⁰ 19ꞌ 50″ E-88⁰ 17ꞌ 40″ E. |
| 3. | Geographical area | 94163 km². |
| 4. | North-South extension in km | 345km. |
| 5. | East-West extension in km | 483km. |
| 6. | Average altitude | 52.73m above the mean sea level. |
| 7. | Geographical Borders of Bihar | North- Nepal South- Jharkhand East- west Bengal West- Uttar Pradesh |
| 8. | Official Languages | 1. Hindi. 2. Urdu. |
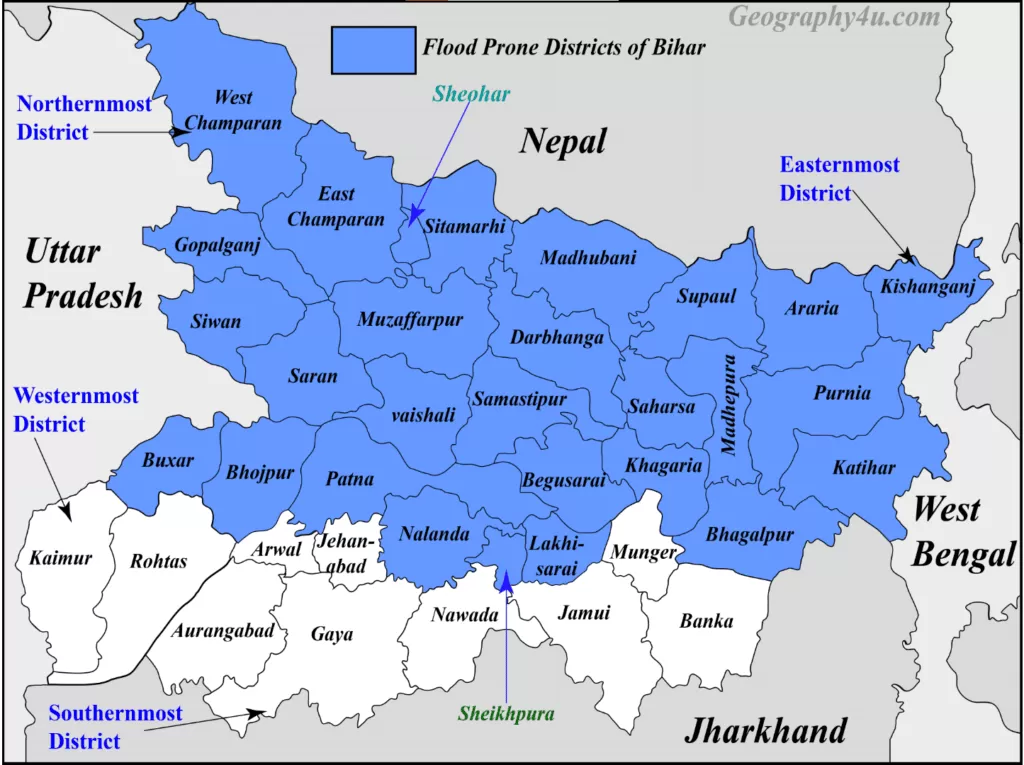
| 9. | Easternmost District | Kishanganj. |
| 10. | Westernmost District | Kaimur. |
| 11. | Northernmost District | West Champaran. |
| 12. | Southernmost District | Gaya. |
Borders of Bihar
| Borders | Districts |
| Districts sharing the borders with Nepal | West Champaran, East Champaran, Sitamarhi, Madhubani, Supaul, Araria and Kishanganj. |
| Districts sharing the borders with Uttar Pradesh | West Champaran, Gopalganj, Siwan, Saran, Bhojpur, Buxar and Kaimur. |
| Districts sharing the borders with West Bengal | Kishanganj, Purnia and Kathiar. |
| Districts sharing the borders with Jharkhand | Rohtas, Aurangabad, Gaya, Nawada, Jamui, Banka, Bhagalpur and Katihar. |
| Districts sharing the borders with Nepal and West Bengal | Kishanganj. |
| District sharing the borders with Patna | Vaishali, Saran, Bhojpur, Arwal, Jehanabad, Nalanda, Lakhisarai, Begusarai and Samastipur. |
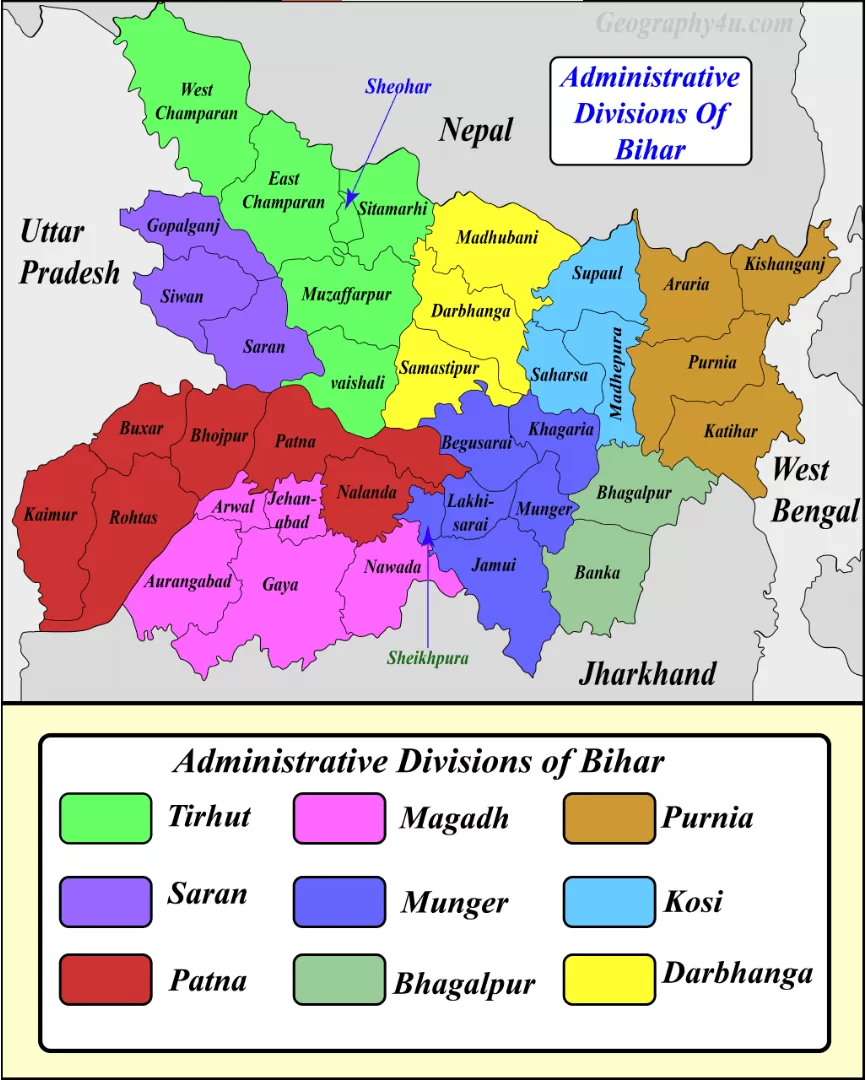
Administrative divisions of Bihar
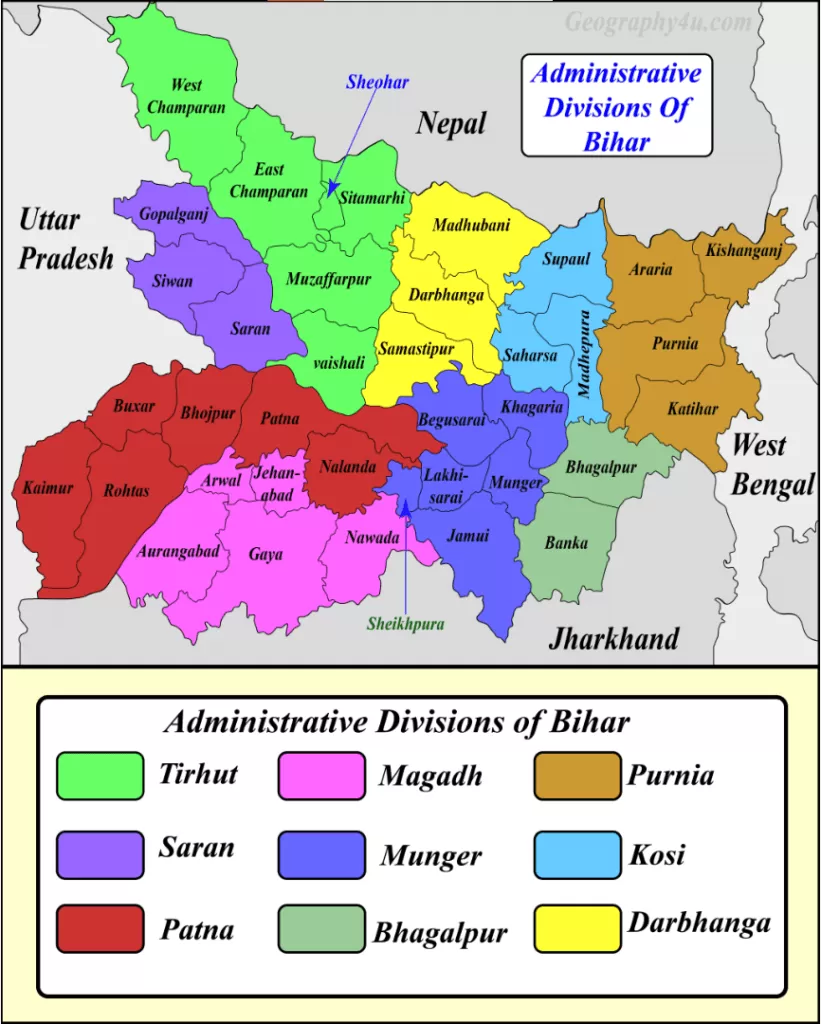
| Divisions | Headquarter | Districts |
| Tirhut | Muzaffarpur | Muzaffarpur, East Champaran, West Champaran, Sitamarhi, Vaishali and Sheohar. |
| Saran | Chapra | Saran, Siwan and Gopalganj. |
| Patna | Patna | Patna, Bhojpur, Bhabhua, Rohtas, Buxar and Nalanda. |
| Magadh | Gaya | Gaya, Jehanabad, Arwal, Aurangabad and Nawada. |
| Munger | Munger | Munger, Begusarai, Khagaria, Lakhisarai, Jamui and Sheikhpura. |
| Bhagalpur | Bhagalpur | Bhagalpur and Banka. |
| Purnia | Purnia | Purnia, Katihar, Araria and Kishanganj. |
| Kosi | Saharsa | Saharsa, Madhepura and Supaul. |
| Darbhanga | Darbhanga | Darbhanga and Madhubani. |
You can download the maps used in this article under the section of the geography of Bihar maps at the end of this page.
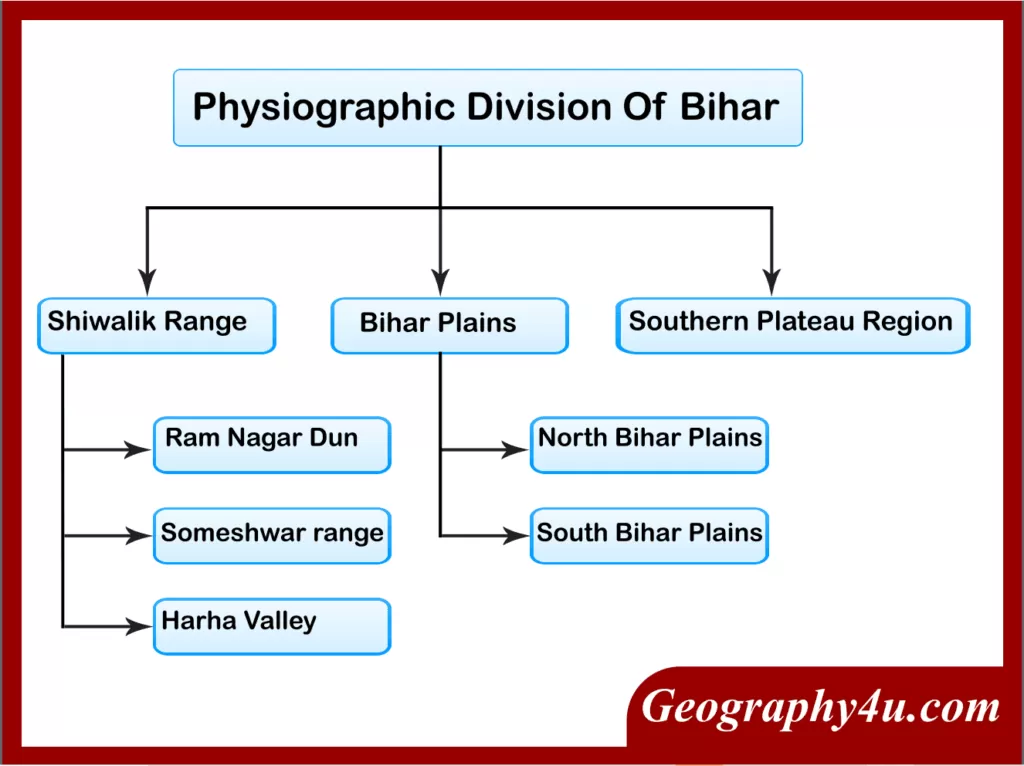
Physiographic division of Bihar
Geologically, Bihar consists of both the younger and older formation of rocks ranges from the Tertiary Period to Pre-Cambrian Period. The plains of Bihar have come into existence by the sediments deposited by the rivers. Geographically, Bihar is bounded by the Himalayan foothills, the Indo-Gangetic plains, the Vindhyan plateau and the Gondwana Basin. Based on the physical and structural conditions, Bihar is divided into three physiographical units.
- The Shivalik Ranges or Shiwalik Ranges.
- The Bihar plains.
- Southern Plateau regions.

Read a complete article on the Mountain Himalaya, its ranges etc. at Geography4u/Mountain Himalaya.
Its also covers about Shiwalik, Great Himalaya and Middle Himalaya etc.
Best books for BPSC
The Shiwalik Range in Bihar
- The Shiwalik range is located in the north-western part of West Champaran.
- It spreads over an area of 32km in length and 6-8km in width.
- Based on the local variations of topography, it can be further divided into the following parts.
Someshwar Range
| Sr. No. | Facts | Features |
| 1. | Extent | From the mouth of Triveni canal up to Bhikhna Thori pass. |
| 2. | Border | It forms a boundary between India and Nepal. |
| 3. | Highest Point | Someshwar Fort (874m). |
Ramnagar Dun
| Sr. No. | Facts | Features |
| 1. | Extent | 214km2 |
| 2. | Location | Southern side of Someshwar Hills marked by broken Hilly region. |
| 3. | Highest Peak | Santpur Peak (240m). |
Harha valley
| Sr. No. | Facts | Features |
| 1. | Extent | 24km in length. |
| 2. | Location | Between Ramnagar Dun and Someshwar Range of Bihar. |
| 3. | Commonly known as | Valley of Barha River. |
Bihar Plains
The Ganga river flows from west to east in Bihar, dividing the state into two unequal halves namely North Bihar plains and South Bihar plains. The plains of Bihar are formed by the silt carried by the Ganga and its tributaries. They are spread over an area of 45000km2.
The North Ganga plains
North Bihar consists of the plains of alluvium north of Ganga, falling between the Ganga and Indo-Nepal border. Generally, the slope of north Bihar is from northwest to southeast. Also, this region has been drained by the rivers of north Bihar.

| Facts | Characteristics |
| Location | Northside of Ganga. |
| Extent | 1. Spread over the whole of Tirhut, Saran, Darbhanga and Kosi division. 2. Ghaghra-Gandak Doab in the west to Mahananda valley in the east. |
| Drainage area | Ghaghra, Gandak, Bhagmati, Kamla, Kosi and Mahananda rivers. |
| Marked by | Chuar formation (Oxbow lakes) |
You can read a complete article on rivers of Bihar at the link below.
geography4u/rivers in bihar
The South Ganga Plains
In terms of the geographical area of Bihar, the South Bihar is spread over 40,070km2. In terms of percentage, it accounts for 42.7% of the total area of Bihar. Demographically, it supports 36.5% of the state’s population. Also, this area is administered under the Magadh, Patna, parts of Munger and Bhagalpur administrative divisions.
The eastern portion of the alluvial plains of South Bihar is interrupted by the Kharagpur Hills. The south plains of Bihar are wider in the west and narrower in the east. Moreover, the western portion of this alluvial plain slopes from southwest to northeast. On the other hand, central and eastern parts of the plain slopes from south to north. The hills of Rajgir have an elevation of 445m. While the Kharagpur range has an elevation of 300m above the mean sea level.
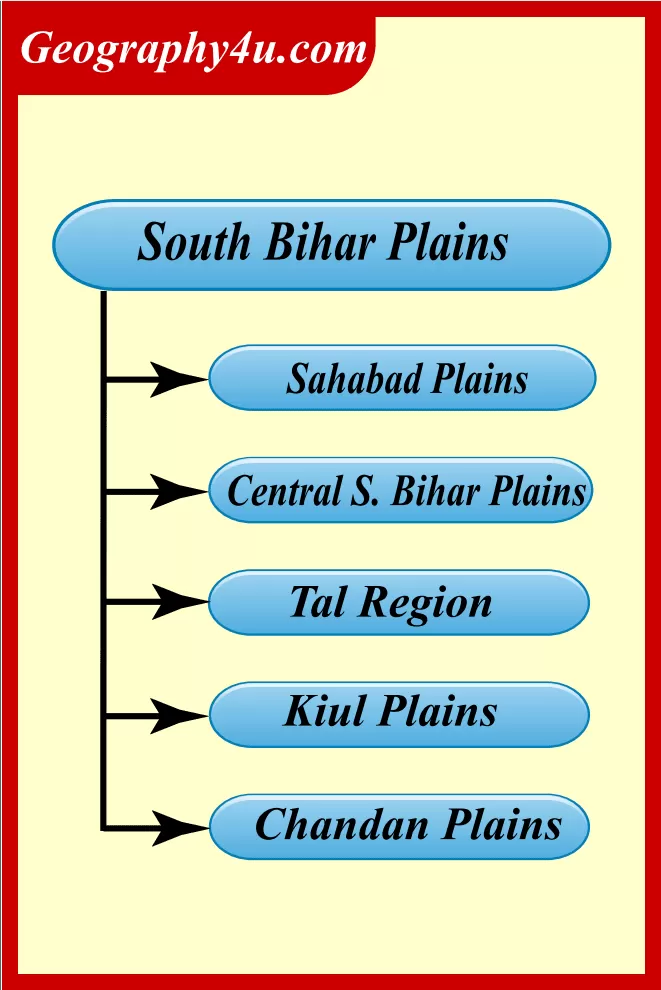
| Facts | Characteristics |
| Extension | 1. From the Ganga up to Chhota Nagpur Plateau. 2. Smaller than North Bihar Plains. |
| Shape | Triangular in shape. |
| Important Hills | Barabar Hills, Rajgir Hills, Giriak Hills, Kharagpur Hills (in the districts of Jehanabad, Nalanda and Munger). |
| Elevation | Higher in the south and slopes towards Ganga. |
South Hilly region of Bihar
- The south Hilly region of Bihar is marked by hills and ridges.
- Geographically, it extends from the Kaimur district in the west to the Banka district in the east.
- Geologically, this region is made up of hard rocks of Genesis, Schist, and Granite.
- The important hills of this region are Pretshila, Jethian, Ramshila, etc.
Soils of Bihar
Being an agriculture-dominant state, the people of Bihar obtain their livelihood from agriculture. Based on the composition, regional distribution, and features, the soils in Bihar are divided into the soils of North Bihar Plains and South Bihar Plains.
Soils of North Bihar
- Piedmont Swamp Soil.
- Terai Soil.
- Recent Alluvium Soil- Khadar and Bhangar.
Soils of South Bihar
- Old Alluvium Soil.
- Tal Soil.
- Balthar Soil.
- Red Sandy Soil.
Important soils of Bihar
| Types of Soil | District | Crops | Chemical Properties |
| Balthar | Kaimur | Jowar, Bajra, Arhar | Sandy, Calcareous and Yellow. |
| Bal Sundari | Saharsa, East and West Champaran | Sugarcane, Wheat, Maize and Tobacco. | Lime and Alkaline. |
| Bhangar | Patna, Gaya and Rohtas | Jute, Sugarcane and Arhar. | Acidic, Rich in Lime. |
| Khadar | Muzaffarpur, Purnia, Saharsa, Darbhanga, Bhagalpur | Wheat, Rice, Gram and Maize. | Dark brown and fertile. |
| Tal | Patna, Munger | Pulses, Oilseeds and Wheat. | Heavy soil. |
| Terai | West Champaran | Sugarcane, Jute and Rice | Sandy and calcareous, Brown and light yellow |
Climate in Bihar
The climate of Bihar is characterized by a humid and subtropical climates. There are three distinct seasons in Bihar (Summer season, Winter Season and Rainy Season). Annual average temperature ranges between 8C in cold winters during December- February to 38C in the hot summer month during April- June.
Agro-Climatic zones of Bihar
The following are the agro-climatic zones of Bihar.
- North-West zone, consisting 13 districts with an annual rainfall of 1040mm-1450mm.
- North-East zone, covering 8 districts having annual rainfall of 1200mm to 1700mm and loam or clay-loam soil.
- South Zone covering, 17 districts, having soil of sandy loam, loamy, clayey or clay-loam and rainfall of 990mm to 1300mm.
Out of the three zones, the north-east zone receives high annual precipitation. Also, the precipitation in this zone is more than 80% during the Kharif season.
Read a full article on types of rainfall and precipitation at – Geography4u/precipitation and rainfall
Frequently asked questions
Which is the largest district of Bihar in terms of area?
West Champaran in Tirhut Division is the largest district of Bihar, having a total geographical area of 5228 sq. km.

Which is the smallest district of Bihar in terms of area?
Sheohar in the Tirhut Division is the smallest district of Bihar, having a total geographical area of 443 sq. km.
Which is the largest river in Bihar?
The Ganges (445km).
Which is the state animal of Bihar?

Ox is the state animal of Bihar.
Which is the state bird of Bihar?

Sparrow is the state bird of Bihar.
Which is the Highest place in Bihar?
The Someshwar Fort (874m).
Which districts had the maximum rainfall in Northern Bihar in 2019?
Kishanganj (1581mm), Siwan (1403mm), and Araria (1310mm) (According to rainfall trends of Bihar in 2019).
Which districts had the least rainfall in Southern Bihar in 2019?
Sheikhpura (580mm), Arwal (545.6mm).
Name the river which is commonly known as Sorrow of Bihar.
Kosi River.
Which are the flood-prone districts of Bihar?

Out of 38 districts, there are 28 districts in Bihar which are flood-prone. These districts have been represented in the map above.
What is the Holy Festival of Bihar?
Chhath Puja
Geography of Bihar maps
- Political map of Bihar.
- Administrative Zones of Bihar.
- Geological map of Bihar.
- Cyclones in Bihar.
- Earthquakes in Bihar.
Read more articles related to the geography of Bihar and India. Also, do share and follow the upcoming articles.







Pingback: Bpsc geography optional syllabus 2022 updated | geography4u
Pingback: Detailed Bpsc syllabus 2022-23 | Geography4u.com