Table of Contents
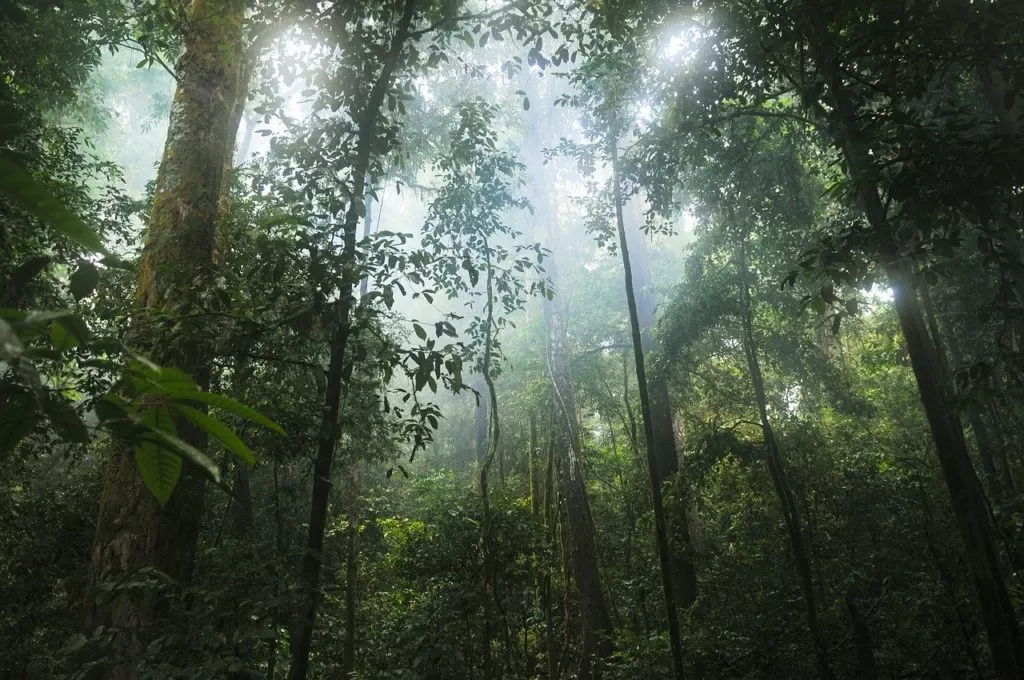
Tropical rain forest
Tropical rainforest biome provides the optimum environmental condition for the growth and development of animals and plants. Most importantly, they receive high rainfall throughout the year. Because of the uninterrupted supply of abundant moisture, this tropical rainforest is also called an optimum biome.

Location and extent of rainforest
- Normally, the tropical rainforest biome extends between 10⁰ N to 10⁰ S latitude.
- The maximum development of these biomes has taken in Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, Indo-Malaysian region.
| Sr. No. | Regions | Extent |
| 1. | Amazon Basin | South America |
| 2. | Congo Basin | Africa |
| 3. | Indo-Malaysian region | Java, Sumatra, Borneo,Malaysia, Guinea |

The climate of tropical rainforest biomes
- The average annual rainfall of the tropical rainforest biome is about 2000 mm or even more.
- The most outstanding feature of tropical rainforest is its great uniformity of temperature throughout the year.
- Mean annual temperature is around 20⁰C.
- The annual range of temperature is around 1‘C.
- However, the daily range of temperature varies between 5⁰C and 10⁰C.
- The upper canopy of trees receives maximum sunlight.
- Indeed, the amount of sunlight decreases downward and it becomes minimum at the ground surface.
- Due to progressively decreasing sunlight, there is a keen competition among the vegetation community for getting sunlight.
- Besides, wind speed also decreases downwards to the ground surface.
- Furthermore, the moisture content in the air increases from the uppermost canopy downwards to the ground surface.
- Almost the absence of sunlight at the ground stratum results in the development of few leaves and flowers.
- Due to paucity of sunlight, the germination of seeds, and seedlings and saplings are slow.
Precipitation
- The precipitation ranges from 1500mm to 2500mm throughout the year.
- Because of the enormous heat in the equatorial belt, the mornings are bright and sunny.
- The tropical rainforests are characterised by all types of rainfall.
- For instance, convectional and orographic rainfall are more often.
- Moreover, cyclonic disturbances also cause rainfall in these forests.
Plants and animals of the tropical rainforest
Composition of species
- The tropical rainforest biome accounts for the largest number of plants species.
- Trees are the most significant member of the tropical rainforests.
- The diversity of plants is great enough that one hectare of land accounts for 40 to 100 species.
- Also, the tree accounts for 70% of the total plant species of these forests.
- Climbers or Creepers are the second important floral members of the rainforests.
- Indeed, the tropical rainforest accounts for 90% of all climbing species.
Vertical stratification of plants in the rainforest biome
There are five layers of strata from the ground surface to the uppermost canopy of the tropical rainforest biome.
1. top most layer
The top surface of the uppermost stratum is like an umbrella. However, the level of the top surface is discontinuous. The height of the topmost layer ranges between 30m and 60m. This layer is also called a Dominant layer.
2. second layer
It develops below the first uppermost layer of the forest canopy at the height of 25m to 30m. It is also called as the Co-dominant layer.
3. Third layer
It consists of lower and smaller trees. The crown of this layer is at the height of 15m to 20m from the ground surface.
4. fourth layer
This layer represents the shrubs which are below the aforesaid three layers. Moreover, this layer is fragmented and sporadic.
5. Ground layer
This layer represents the plants growing at the ground surface, seldom gain the height more than a meter. However, herbaceous plants and ferns dominate this layer. Moreover, herbaceous plants do not form dense cover due to the absence of light.
| Sr. No. | Important trees |
| 1. | Mahogany |
| 2. | Ebony |
| 3. | Greenheart |
| 4. | Dye woods |
| 5. | Palm trees |
Tropical rainforest animals
- Due to the regular growth of the plants, there is a regular supply of abundant food for the animals throughout the year.
- Because of the constant supply of food, the animals of tropical rainforest biomes are least mobile.
- The animals of different species live in the various vertical strata of the forest.
- These forests are full of animal activities throughout the day and night.
- Moreover, there is always hue and cry in these rain forests which make this biome alive.
- Most of the animals are arboreal.
- Besides, these arboreal animals have been provided with additional features to climb the trees.
- For instance, they have claws with adhesive pads and several climbing mechanisms.
- Mammals of these biomes have generally smaller and sturdy bodies.
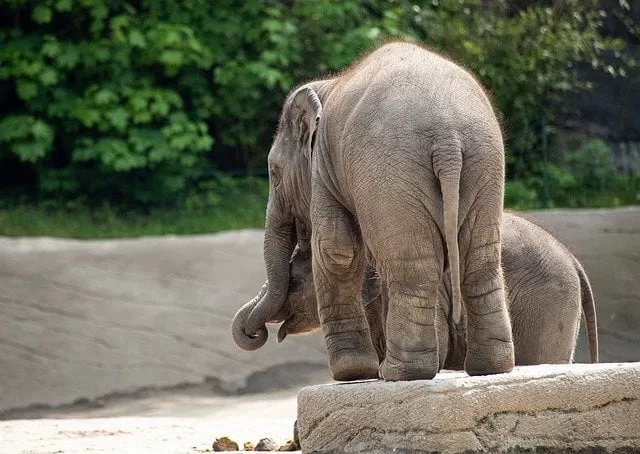
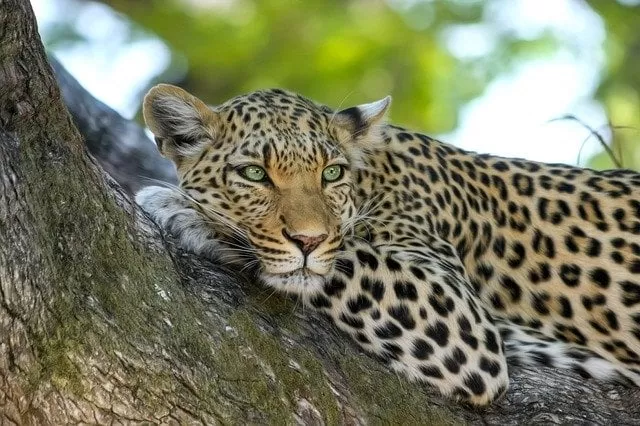
- Some of the animals of the rainforest include chimpanzee, gorilla, bison, Elephant, okapi, leopard, Pigs etc.
- The number, diversity of animals and density in the tropical rainforest biome increase from the ground layer towards increasing strata.
- However, the largest animals of the tropical rainforests are smaller in size than their counterparts in other open forests and grasslands.
- For example, the forest elephants of the rainforest biome are much smaller in size than the savanna elephants.
Plants in tropical rainforests

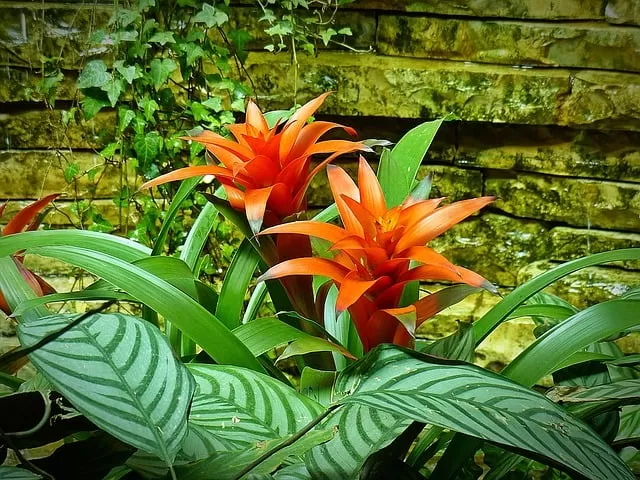
Bromeliad flower 
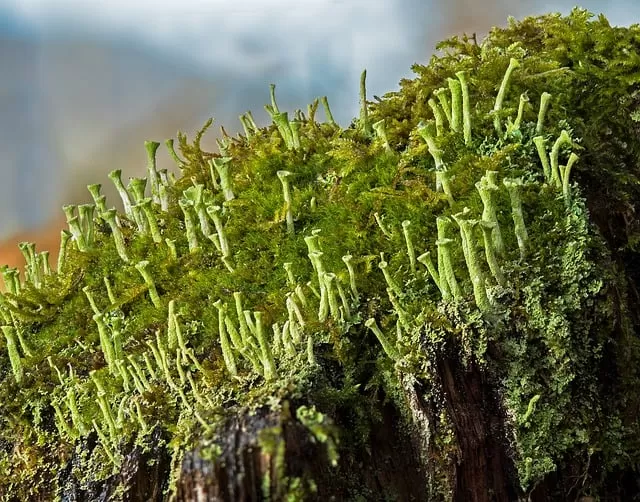
Lichens 
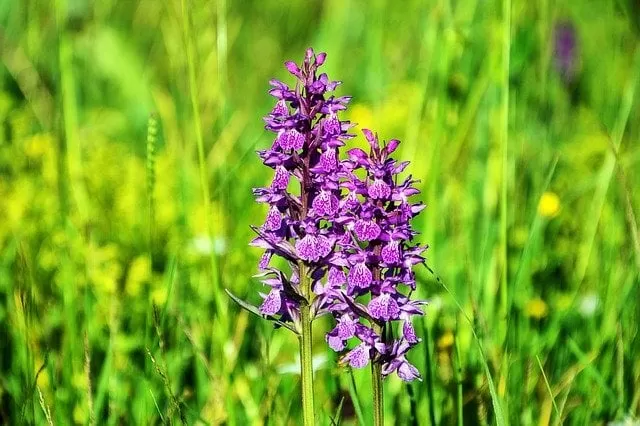
Orchids 
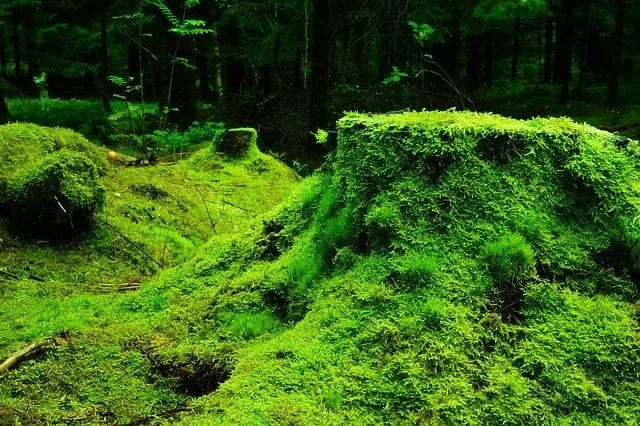
Mosses 
Tall trees 
Dense forset
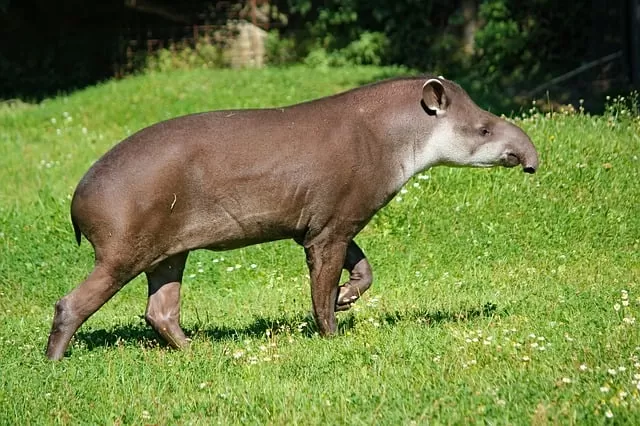
Animals of tropical rainforest

Monkey 
Elephants 
Gorilla 
Leopard 
Okapi 
Rhino 
Tapir
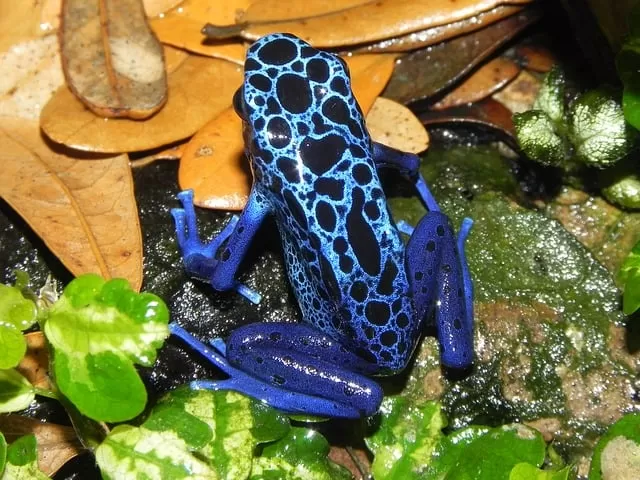
Reptiles of the Rainforest biome

Crocodile 
Dart frog 
Chameleon 
Snakes
Birds of tropical rainforest

Eagle 
Flying fox 
Grey parrot 
Macaw
Insects of tropical rainforests

Grasshopper 
Bugs 
Spiders 
Butterflies
Life and development in the tropical regions
- These biomes are sparsely populated.
- Moreover, most of the people live as hunters and gatherers.
- Also, they often practice shifting cultivation.
- The ever-flowing rivers and streams provide an inexhaustible supply of fresh water.
- The advent of the European in these regions, establish the plantation in the Sumatra, Malaysia, Java, West Africa and Central America.

Tribes and their occupation
| Tribes | Occupation |
| Tribes of Amazon Basin | Collect wild rubber |
| Pygmies of Congo Basin | Gather nuts |
| Orang Asli of Malaysian forest | Make Cane products |
High value crops
| Name of the crop | Leading producer |
| Natural rubber | Malaysia and Indonesia |
| Cocoa | Ghana and Niger |
| Palm oil | Indonesia and Malaysia |
Other crops– Coconut, Sugarcane, Coffee, Tea, Tobacco, Spices, Cinchona, Banana, Pineapple.
Lumbering
The tropical rainforest biomes have great potential in timber resources. However, the commercial extraction of timber is difficult. As an illustration, these hardwoods are too heavy to float in the rivers.
Factors which affects the life in rainforest biome
Climate and health
- Excessive heat and humidity cause sun strokes.
- Prevalence of diseases like yellow fever and malaria.
Spreading of bacteria and pests
- The hot and humid climate encourages the spreading of insects and pests.
- Consequently, these organisms cause both disease and injuries to crops.
HINDRANCES in the tropical Rainforest
- Due to dense forests, clearing a small patch of land is quite difficult.
- Also, the construction of roads and railways is impracticable due to high maintenance cost.
- The rivers are the only means of communication.
In brief, the tropical forests are shrinking day by day due to the adverse impact of human activities. According to International World Wildlife Fund (WWF) species of the tropics are at danger.