In this article, I will discuss the floods in Bihar, the causes, and the effects of floods in Bihar with the help of maps and diagrams. This topic is very important for the Geography optional of bpsc. After reading this article you will get a crisp idea about the factors which trigger the intensity of floods in Bihar.

Gandak River between Bihar and Nepal
Flood is a high flow of water which overtops either the natural or the artificial banks of a river channel.
Smith
Table of Contents
Floods in Bihar
The Topography of Bihar is marked by several perennial and non-perennial rivers, originating from the Mountains of Himalayas. These rivers carry high sediment loads that are deposited on the Bihar’s Plains. Also, Bihar is one of the climate-sensitive states in India. Bihar receives maximum rainfall during the southwest monsoon, lasting from June to September. Consequently, the onset of the monsoon in Bihar causes flood-like situations, especially on the northern plains of Bihar. Besides, climate change and global warming increase the frequency and intensity of both the floods and droughts in Bihar.
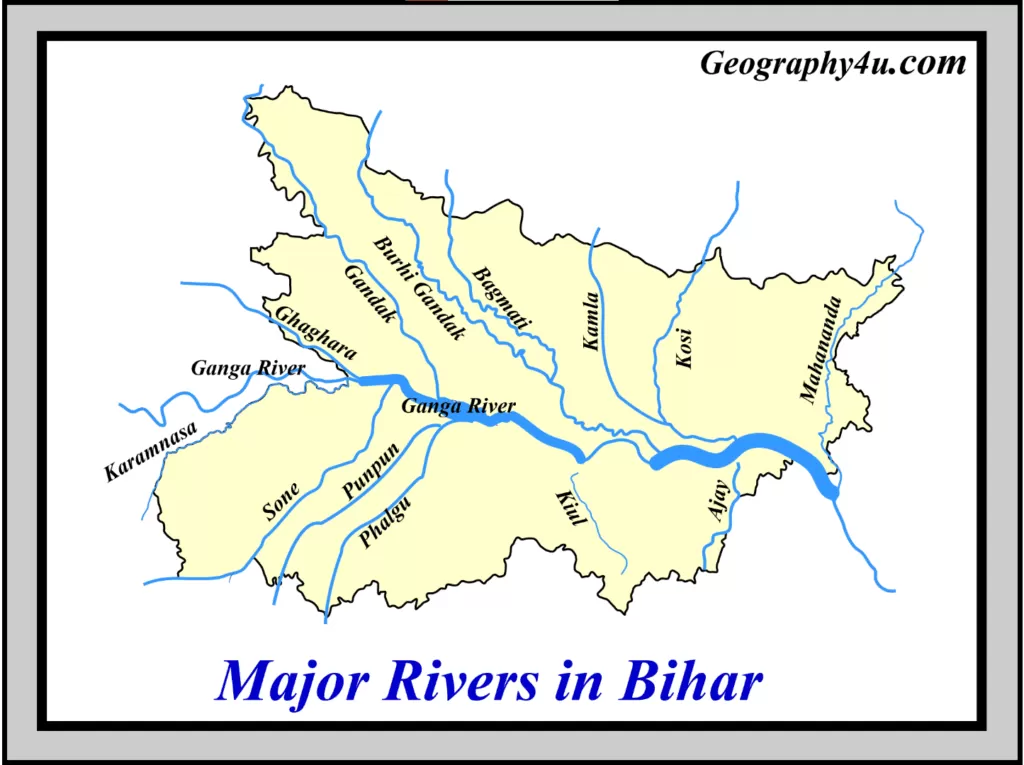
According to the government of Bihar Flood Management Information System Cell, the floods in Bihar can be divided into four categories.
- Class-1: Flash floods due to abundant rainfall in Nepal.
- Class-2: River floods
- Class-3: Congestion of drainage in river confluence.
- Class-4: Permanently water-logged area.
Geographically, 73.63% of the area of north Bihar is prone to floods. Out of 38 districts of Bihar, 28 districts are affected with floods which cause a huge loss of property, lives, and Infrastructure. Out of 28 flood-affected districts of Bihar, 15 districts are worst affected. As per Rashtriya Barh Aayog (2006), it has been estimated that about 24% of the total flood-affected population of India resides in the flood plains of Bihar.
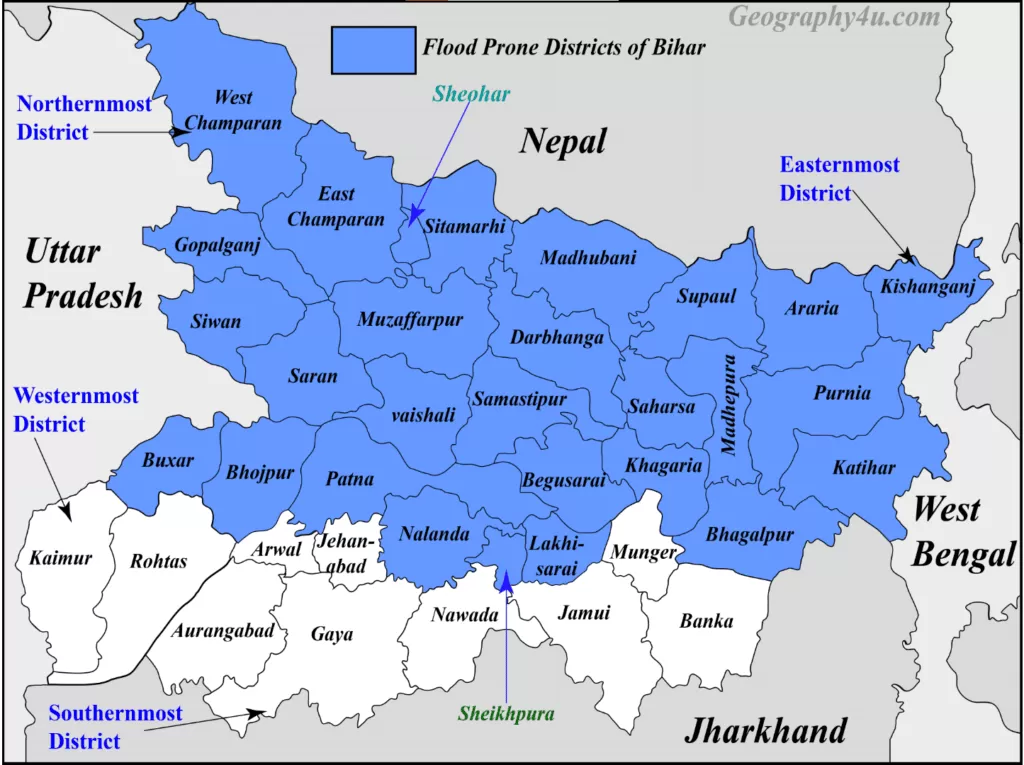
In the Years of 1978, 1987, 2002, 2004, 2007 and 2008, Bihar witnessed a high magnitude of floods. The floods in Bihar during July to September 2019 affected 13 districts.
Read a complete article on the geography of Bihar with maps and charts.
Extremely flood-prone districts of Bihar
| Muzaffarpur |
| Vaishali |
| Sitamarhi |
| Sheohar |
| Darbhanga |
| East Champaran |
| Madhubani |
| Samastipur |
| Saharsa |
| Supaul |
| Madhepura |
| Khagaria |
| Bhagalpur |
| Katihar |
| Darbhanga |

The 13 districts affected by floods in Bihar (2019)
- Sheohar.
- Sitamarhi.
- East Champaran.
- Madhubani.
- Araria.
- Kishenganj.
- Supaul.
- Darbhanga.
- Muzaffarpur.
- Saharsa.
- Katihar.
- Purnea.
- West Champaran.
Factors responsible for floods of Bihar
- Large scale deforestation in the upper catchment areas reduces the infiltration of rainwater. Consequently, it increases the tendency of the magnitude of floods in Bihar.
- Construction of roads, buildings, pavements and courtyards also reduces the infiltration of rainwater.
- Due to the increase of urbanisation, the process of cementation is increasing day-by-day.
- Poor drainage system.
- Heavy rainfall for a longer period.
- The bursting of clouds.
- Massive erosion along the river banks.
- Shifting of river channels.
- Deposition of silt, sand and clay in the flood plains.
- Choked drains and nallas.
Steps to control floods in Bihar
- The afforestation in the upper catchment areas reduces the magnitude of floods in Bihar by binding the soil into the roots of trees.
- To reduce the volume of floodwater by making reservoirs, wells and ponds.
- By clearing the sediments deposited in the river beds.
- By reducing the slopes of the topography of the flood-affected area of Bihar.
- Formation of channels to allow quick discharge of water.
- By converting the steep slopes into terraces.
- By increasing the flood-affected area under mangroves.
- Using modern and precise estimating and forecasting tools.
- Cementation of both the sides of the riverbank to reduce the chances of lateral erosion caused by the river.
- Diversion of floodwater in the low-lying areas or artificial channels by dykes, walls and stone spurs.
Government Initiatives to reduce the floods of Bihar
- The government of Bihar has provided the modern rescue operation kits to the flood-prone districts.
- Providing ten motorboats to each of 28 flood-prone districts of Bihar.
- The national disaster response force (NDRF) team is proving training to home guards of Bihar.
- The state government has started construction of 200 flood shelters in the flood-affected districts of Bihar.
- Master trainers have been trained by NDRF in Bihar for search and rescue operation, first aid, capacity building and awareness campaign.
- Various projects on inter-linking of rivers have been planned.
Inter-linking of rivers to reduce floods of Bihar
The National Water Development Agency (NWDA) has proposed thirty major river link canals in India to transfer the water from surplus region to water deficit region. Out of these 30 major river link canals, six are directly related to Bihar.
Inter-linking canals directly related to Bihar
The following are the inter-linking canals related to Bihar.
- Kosi-Mechi Link Canal.
- Kosi-Ghaghara Link Canal.
- Sone dam-southern tributaries of Ganga Link Canal.
- Chunar-Sone Barrage Link Canal.
- Brahmaputra-Ganga (Manas-Sankosh-Teesta-Ganga) Link canal.
- Gandak-Ganga Canal.
Floods are indeed the natural phenomenon and one cannot entirely get rid of them but, their frequency and impact can be reduced through proper management by using human resources, better warning systems and various control measures.


Pingback: Agriculture of Bihar: problems & solutions | Geography4u.com
Pingback: Bpsc geography optional syllabus 2022 updated | geography4u