Table of Contents
Introduction
We all are familiar with the word forests, but only a few people know what are the types of forests around us. So, In this article, I will discuss deciduous forests, their location, and distribution. Also, the animals and plants of deciduous forests around the world. These forests play a vital role in the overall ecological balance of the environment. It is an abode of many plants and animals, as these forests have their economic significance. After reading this article, you will easily understand the characteristics of deciduous forests and how they are different from tropical rainforests.
What are deciduous forests?
Deciduous forests are forests that shed their leaves to withstand drought. The natural vegetation of these forests depends on the amount of precipitation. These forests are more open and less luxuriant than the equatorial evergreen forests. Most of these forests yield valuable timber. These biomes are endowed with durable hardwood.
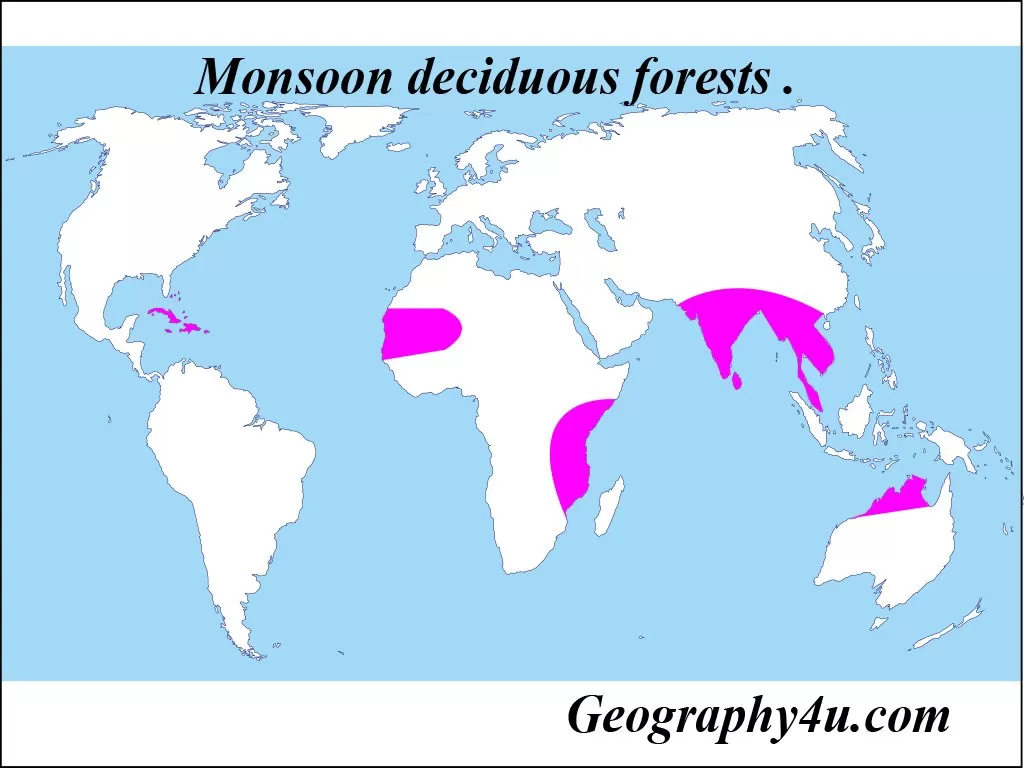
Location of deciduous forests
The tropical deciduous forests are found in the regions of monsoon climate. There are three areas of tropical deciduous forest biomes viz.
- The Neo-tropics mainly West Indies.
- Indo-Malaysian Zone.
- Eastern Africa and northern Australia.
Climatic conditions of deciduous forest
- The tropical deciduous forest biome is characterized by two distinct seasons’ viz. moist season and dry season.
- There are three main seasons in a year in India and surrounding monsoonal areas such as Pakistan, Bangladesh, etc.
- On average, the mean annual rainfall is around 1500mm.
- Tropical deciduous forests are the most widespread forests in India.
- There are many variations in the temporal and spatial distribution of rainfall.
- There is maximum evaporation during warm dry summer months which results in a marked reduction in soil water.
- About 80% of the annual rainfall is received within three months of the summer season (July, August, and September).
- The evaporation rate is maximum during the warm dry summer months which results in the reduction of soil water.
Types of deciduous forests
There are two types of deciduous forests viz. the moist and dry deciduous forest.
Moist deciduous forests
The moist deciduous forests are widespread in the regions that record rainfall between 100-200 cm. Teak, Sal, Rosewood, Mahua, Gooseberry, sandalwood, etc. are the main species of these forests.
Dry deciduous forests
Dry deciduous forest covers vast areas of India, where rainfall ranges between 70 -100 cm. Bastard teak, Cassia, Aegle Marmelos, Senegalia catechu, Axlewood, etc. are the common trees of these forests.
Climatic conditions tropical Monsoon lands
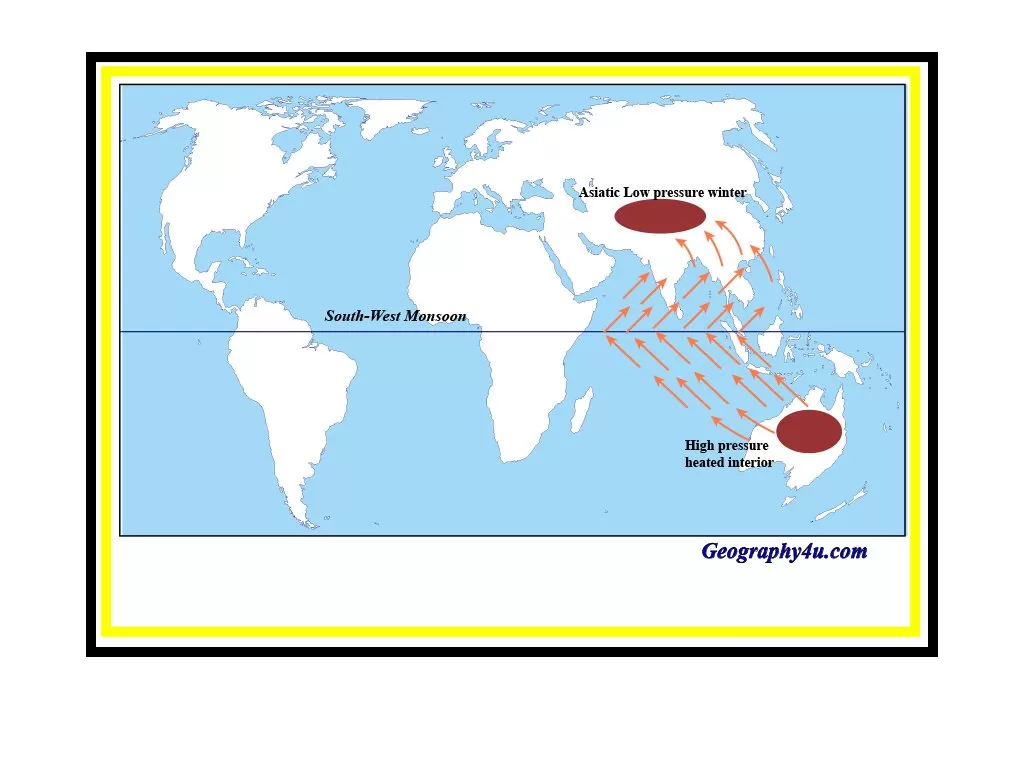
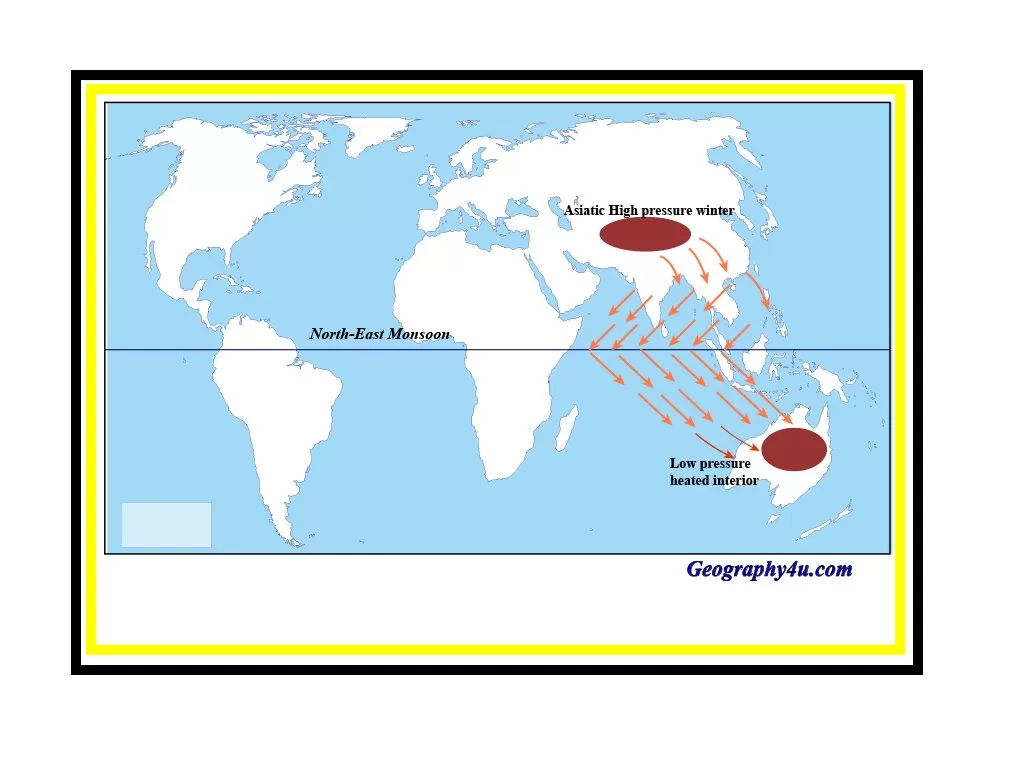
Plant community and structure.
- The number of plant species is less in the tropical deciduous forest biome than the tropical evergreen rain-forest biome.
- The density of plants is lower in this biome than the rainforest biome.
- The average height of trees ranges between 12 m to 30 m.
- Most of the forests yield valuable timber like teak.
- Burma alone accounts for as much as three-quarters of the World’s production of Teak.
- Teak is used for shipbuilding, furniture and other constructional purposes.
- Other kinds of timber include Sal, Acacia and some varieties of Eucalyptus.
- There are four layers in the vertical structure of the tropical deciduous forests.
- The uppermost and the second strata consist of trees.
- The third stratum is formed by shrubs whereas the fourth stratum represents the herbaceous plant.
- Most of the trees are deciduous but the shrubs of the third stratum are evergreen.
Agricultural development in the monsoon lands




- To support a dense population, much of the monsoon forest has been cleared.
- The monsoon lands deeply reflect the intensity of man’s quest for subsistence.
- The plains are ploughed extensively for agriculture.
- Overexploitation of deciduous forest resulting in acute soil erosion.
Shifting cultivation in deciduous forests
- It is the most primitive form of farming which is widely practised.
- The tribesmen move to a new clearing when their first field is exhausted.
- The clearing of forests mainly made by fire.
- The crops are left entirely to the care of nature.
- Farmers use simple tools like hoes and sticks for ploughing and seeding.
- Maize, dry paddy, yams and sweet potatoes are the most common crops.
- Farming is entirely for subsistence.
| Local name | Different countries |
| Ladang | Malaysia |
| Taungya | Burma |
| Tamrai | Thailand |
| Caingin | Philippines |
| Human | Java |
| Chena | Sri Lanka |
| Milpa | Africa and Central America |


Animal life in deciduous biomes
- There are lesser number of animal species in the monsoon forests than the rain-forests.
- Due to less developed vertical strata, the diversification of animals is less.
- The shedding of leaves, drying of herbaceous plants affect the seasonal behaviour of animals.
- Deciduous biomes represent the largest number of domesticated mammals.
- Birds in the East Africa breed twice during the two different seasons of a year.
- These biomes carry the largest number of human populations of the world.
Man, and the monsoon deciduous forest
- These forests have been destroyed within the last 50 years through the rapacious utilization of forest resources for commercial purpose.
- The rapid rate of deforestation has led to the invitation of several ecological and geological problems.
- Several species of plants and animals have been extinct due to deforestation and mass hunting.
Distribution of tropical rainforest pdf
Read more articles
- How did the theory of plate tectonics evolve over time?
- 7 Criticisms of Continental Drift Theory by Alfred Wegener
- Malthus theory of population: critical analysis & relevance
- Major Types of Clouds formation and their Characteristics
- Get Detailed Bpsc syllabus 2022-23
If you like this post, kindly give your reviews in the comment section. Also, keep share these articles more so, everyone can take benefits from it.
