In this article, I will discuss the important climate zones in India with the help of Maps. The climate zones in India help us to determine the selection of crops which are suitable to the elements of climate for a region. Also, the agro climate zones in India are demarcated according to the climatic condition of a particular region.
Table of Contents
Introduction
In countries like India, agriculture plays a vital role in the overall economy of the nation. According to the 2011 census, about 54.6% of Indian population directly or indirectly engaged in the agriculture and allied activities. Hence, the climate of India becomes one of the most significant factors for deciding the cropping pattern in India. Broadly speaking, India has a tropical monsoon climate. However, there are many regional variations in the elements of the climate in India. For instance, rainfall, temperature, humidity, wind velocity, etc. Out of these climatic elements, geographers gave more importance to rainfall pattern than the temperature.
Blanford was the first geographer who attempted to demarcate the various climate zones in India. Besides Blanford, Dudley Stamp, Wladimir Koeppen, Trewartha etc. also attempted to give the classification of the climate zones in India.
Classification of climate zones in India according to Dudley Stamp
Stamp used 18⁰C isotherm of monthly temperature for January to demarcate the two climatic regions in India i.e. Temperate or Continental zone in northern India and the Tropical zone in southern India. These two climatic regions are further divided into eleven sub-regions depending upon the quantity of precipitation and temperature.
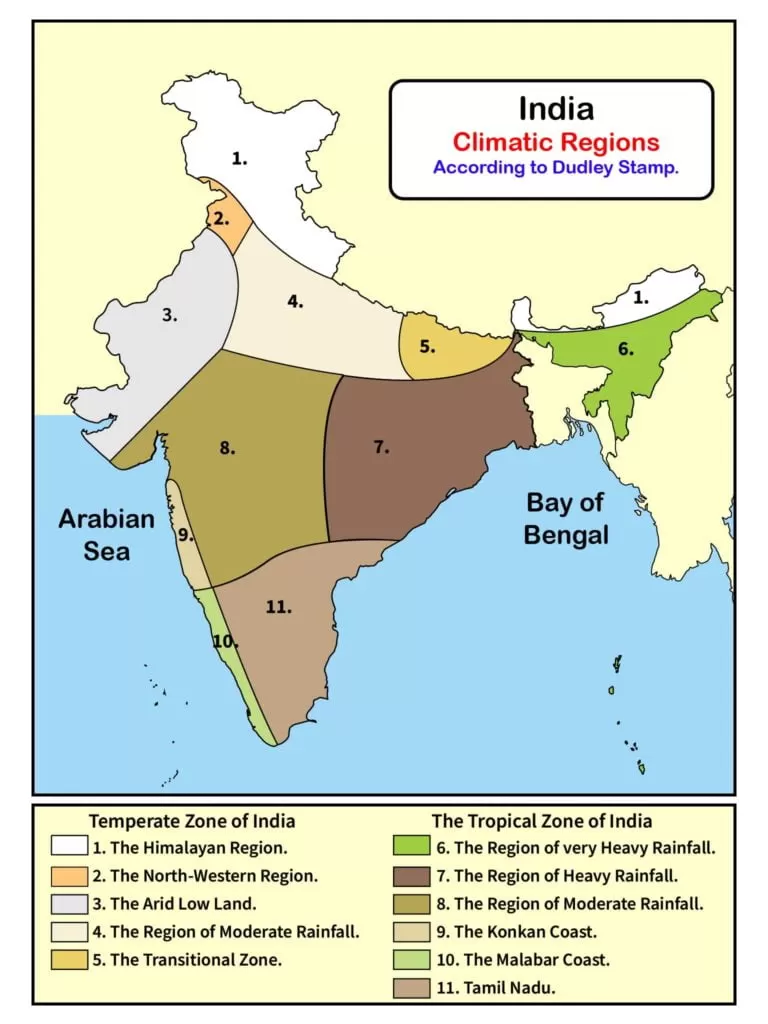
The Climatic zones of Temperate or Continental India
- The Himalayan region (Heavy rainfall).
- The North-western region (moderate rainfall).
- The Arid low land.
- The region of Moderate rainfall.
- The Transitional Zone.
The climatic zones of Tropical India
- The region of very heavy rainfall.
- The region of heavy rainfall.
- The region of moderate rainfall.
- The Konkan Coast.
- The Malabar Coast.
- Tamil Nadu.
The Himalayan region
The Himalayan region spreads over the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, West Bengal, large parts of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir (U.T). During winter, the temperature of this region may reach around 4⁰C to 7⁰C while the summer temperature is around 13⁰C to 18⁰C. The eastern Himalayan region receives more rainfall around 200cm or more. However, the western Himalayan region receives less rainfall around 125cm.
The North-western region
The North-western region includes the northern parts of Punjab and some southern parts of Jammu and Kashmir (U.T). The winter temperature of this region is around 16⁰C while the summer temperature is around 24⁰C. Unlike the Himalayan region, the north-western region receives less rainfall around 40cm.
The Arid land
The Arid land includes the Indian desert (Thar desert), south-western parts of Haryana and the Kutch of Gujarat. The average temperature in winter is between 16⁰C to 24⁰C. This region shows the characteristics of continentality hence, the summer temperature of this region shoots up to 48⁰C. The average annual rainfall of this region is below 40cm. Also, this region is marked by sand dunes.
The region of moderate rainfall
The region of moderate rainfall includes the parts of Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT), the north-western plateau of Madhya Pradesh and the eastern parts of Rajasthan. In general, this region receives the average rainfall between 40cm to 80cm. The average winter temperature in January of this region is between 15⁰C to 18⁰C however, the summer temperature in July may reach between 33⁰C to 35⁰C.
The Transitional zone
The Transitional zone includes the eastern parts of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Geographically, this region lies between the region of moderate rainfall in the west and the area of heavy rainfall in the east. The average annual rainfall of this region is between 100cm to 150cm. The average temperature during the summer in July is between 30⁰C to 35⁰C. On the other hand, the average temperature during the winter in January is between 15⁰C to 19⁰C.
The region of very heavy rainfall
The region of very heavy rainfall includes the states of Meghalaya, Assam, Tripura, Mizoram, Nagaland and Manipur. The average annual rainfall of this region is more than 200cm. During winters, the temperature in January remains around 18⁰C while the summer temperature in July remains between 32⁰C to 35⁰C. Cherapunji and Mawsyaram in Meghalaya receive the maximum rainfall in this region.
The region of heavy rainfall
The heavy rainfall region includes the states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and the parts of north-eastern Andhra Pradesh. The average annual rainfall of this region is about 100cm to 200cm. In general, the trend in rainfall in this region decreases from the east to west region. In January the temperature of this region ranges between 18⁰C to 24⁰C while the temperature in July ranges between 29⁰C to 35⁰C.
The region of Moderate rainfall
The region of Moderate rainfall receives the rainfall between 50cm to 100cm, lying between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats. Due to a rain shadow region, it receives less rainfall compared to the Western Ghats. During winters, the average temperature of this region is about 18⁰C to 24⁰C while the temperature during summer is more than 32⁰C.
The Konkan Coast
Lying parallel to the south-west monsoon winds, the Konkan coast receives rainfall more than 200cm. The Konkan coast enjoys the moderating effect of Arabian Sea hence, the temperature of this region ranges between 24⁰C to 27⁰C.
The Malabar Coast
The Malabar coast extends from Goa in the north to Kanyakumari in the south. Since Western Ghats act as a barrier, the summer monsoon winds in India, originated in the Arabian Sea strikes perpendicular to it and cause high rainfall in this zone. It receives the rainfall over 250cm. Like the Malabar coastal region, it also enjoys the moderating effect of the Arabian Sea.
Tamil Nadu
This region includes the state of Tamil Nadu and adjoining areas of Andhra Pradesh. The average rainfall in this zone ranges between 100cm to 150cm. It remains devoid of south-west monsoon winds of India and receives negligible rainfall due to it. However, it receives the rainfall in November and December from the north-east monsoon winds (retreating monsoon in India). In general, the temperature of this region ranges around 24⁰C.
The Climate Zones in India according to Koeppen’s Classification
Unlike Dudley Stamp, the Koeppen Classification on the climate of India is based on the monthly values of both the temperature and the precipitation. Broadly speaking, Wladimir Koeppen demarcated five major climate zones in India. However, he further subdivided these climatic regions of India into sub-types.
The following are the five major climate regions according to Koeppen’s scheme
- Tropical Climate
- Dry Climate
- Warm temperate climate
- Clod temperate climate
- Ice Climate
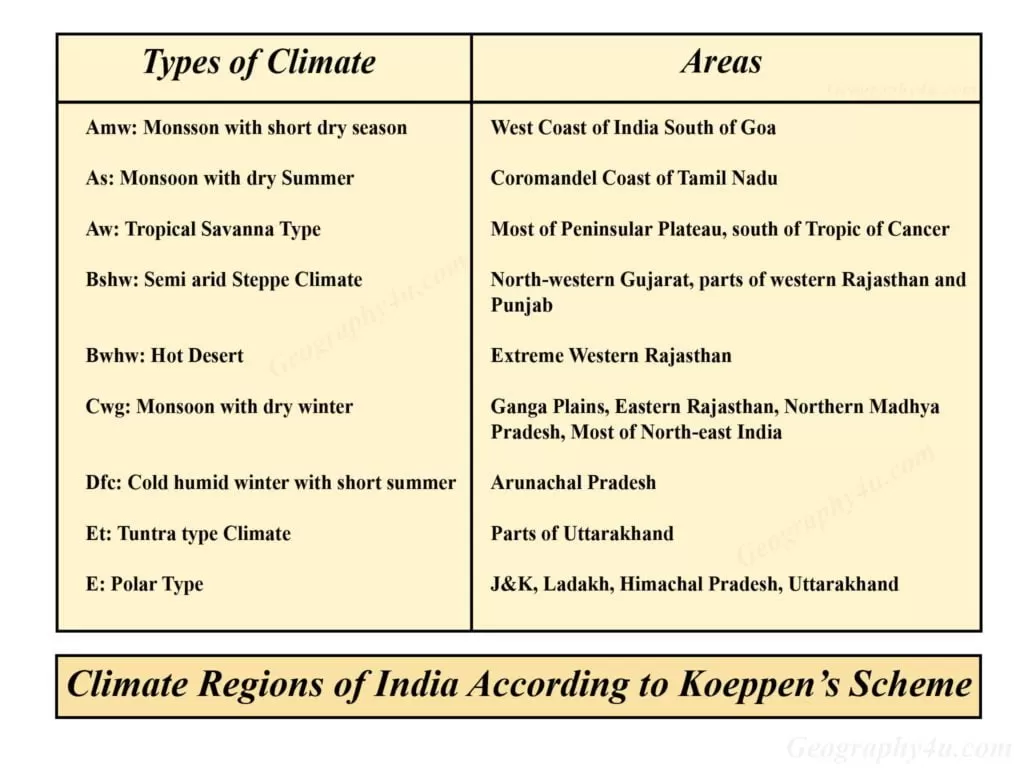
The 9 climate regions in India according to Koeppen Classification
- Amw: Monsoon type with the short dry winter season.
- As: Monsoon type with a dry season in the summer season.
- Aw: Tropical Savanna type.
- Bshw: Semi-Arid Steppe type climate.
- Bwhw: Hot Desert type climate.
- Cwg: Monsoon with dry winter.
- Dfc: Cold, Humid winter with short summer.
- Et: Tundra type.
- E: Polar Type.

Amw: Monsoon type with short dry winter season
Monsoon type with short dry winter season is found in the western coastal regions of India and the south of Goa. Annually, the average rainfall of this region is about 300cm in the summer during the south-west monsoon.
As: Monsoon type with dry season in summer
This type of climate region is found where the rainfall occurs during the winters and the summer is dry. It receives the average annual rainfall between 75cm to 100cm during the retreating monsoon. Geographically, this region lies in the Coromandel coast of Tamil Nadu.
Aw: Tropical Savanna type
This type of climate is found in parts of peninsular plateau. Generally, it receives rainfall during the south-west monsoon. The average rainfall of this region is about 75cm. However, the winters are dry in this climate zone.
Bshw: Semi-Arid Steppe Type
Semi-Arid steppe type climate is found in north-western Gujarat, some parts of Western Rajasthan and Punjab. The average rainfall of this region ranges between 12cm to 25cm. In terms of natural vegetation, it has the arid-steppe type of vegetation (mainly fodder and grasses for cattle).
Bwhw: hot desert type
The hot desert type of climate is found in the parts of extreme western Rajasthan where there is a predominance of deserts. Due to excessive temperature, the natural vegetation is almost absent. In terms of precipitation, it receives the rainfall less than 12cm.
Cwg: Monsoon type with dry winters
The climate of monsoon type with dry winter is found in most of the parts of Ganga Plain, Eastern Rajasthan, Northern Madhya Pradesh and most of north-east India. The summer and the winter temperature of this region are about 40⁰C and 27⁰C respectively. Most of the rainfall occurs in the summer season during the onset of south-west monsoon. Also, it receives rainfall between 100cm to 120cm.
Dfc: cold, humid winter with short summer
This type of climate is found in the Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim and parts of Assam, where the winters are cold, humid and of longer duration. Annually, the average rainfall of this region is more than 200cm. During winters, the average temperature of this region is about 10⁰C.
Et: Tundra type
The Tundra type of climate in India is found in the mountainous regions of Uttrakhand, where the average temperature is about 0⁰C to 10⁰C. Also, there is a fall in the temperature with altitude.
E: Polar type
The Polar type of climate is found in the states of Uttrakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir (U.T). Due to extremely low temperature, the precipitation in this region occurs in the form of snow. Also, the temperature of the warmest month ranges from 0⁰C to 10⁰C.

